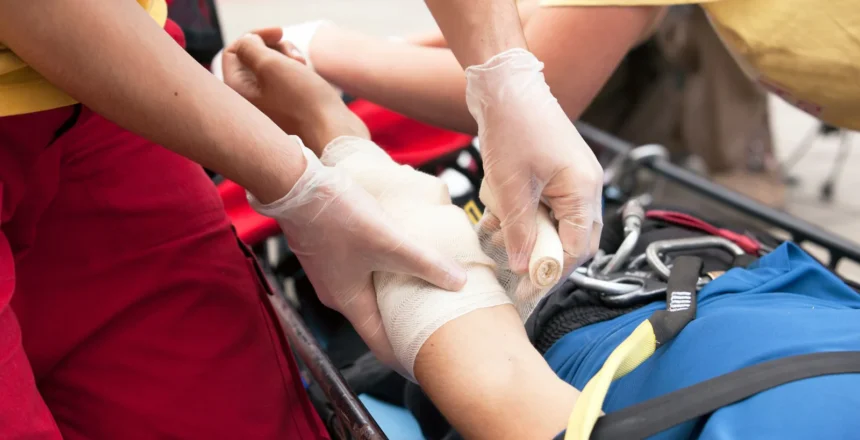
In emergency situations, major traumatic injuries can happen unexpectedly, and knowing how to respond with advanced first aid techniques is crucial for saving lives. Whether it’s a serious fall, car accident, or any other trauma, immediate and effective treatment can drastically improve the chances of survival. Learning how to treat these injuries properly ensures that you can act quickly and competently while awaiting professional medical help.
If you’re looking to gain advanced first aid skills for treating severe trauma, Advanced First Aid: Treating Major Traumatic Injuries provides the training needed to handle these life-threatening situations with confidence.
Understanding Major Traumatic Injuries
Major traumatic injuries are those that involve significant harm to the body, often including broken bones, severe bleeding, burns, or head injuries. These injuries can result in substantial blood loss, shock, and other complications. It’s crucial to understand the different types of major trauma so that you can provide the correct treatment:
- Severe Bleeding: Large, deep cuts or wounds that may lead to significant blood loss.
- Fractures: Broken or dislocated bones, especially in the limbs or ribs.
- Head Injuries: Brain injuries, concussions, or open wounds on the head.
- Burns: Severe burns to the skin and tissue that require immediate care.
- Chest Trauma: Damage to the chest cavity, lungs, or heart from blunt force or penetration.
Each of these injuries requires prompt attention and specific first aid techniques to stabilize the injured person until medical professionals can take over.
Step 1: Assess the Situation
When responding to a major traumatic injury, the first step is to assess the situation. This will allow you to determine the severity of the injury and decide what actions are necessary.
- Ensure Safety: Always make sure the scene is safe before approaching the injured person. Check for hazards such as traffic, electrical wires, or unstable structures.
- Check for Immediate Threats: Assess if there are any life-threatening injuries, such as severe bleeding or difficulty breathing. If the person is not breathing or there is no pulse, start CPR immediately.
- Call for Help: In cases of major trauma, call emergency services as soon as possible. Provide as much detail as you can about the situation, including the injury type, location, and number of people involved.
Step 2: Treating Severe Bleeding
Severe bleeding is one of the most common complications in traumatic injuries. To prevent excessive blood loss, you should apply immediate first aid for severe bleeding.
- Apply Direct Pressure: Use a clean cloth, bandage, or even your hands to apply direct pressure to the wound. Maintain pressure to control the bleeding.
- Use a Dressing: If the cloth or gauze becomes soaked with blood, do not remove it. Add more layers and continue applying pressure.
- Elevate the Wound: If the injury is on a limb, elevate it to a position above the heart level to reduce blood flow to the area and minimize blood loss.
- Consider a Tourniquet: If the bleeding is severe and cannot be controlled with pressure alone, a tourniquet may be required. However, this should only be used as a last resort and by someone who has been trained in its application.
Step 3: Immobilize Fractures
Fractures, especially those involving limbs, can lead to complications such as bleeding, nerve damage, and more severe injury if not handled correctly.
- Support the Injured Area: If you suspect a broken bone, try not to move the affected area. Support the injured limb by using any available material (such as a splint or rigid object).
- Immobilize the Joint: If the injury involves a joint (such as an elbow or knee), try to stabilize it by keeping it in a neutral position and avoiding any movement.
- Apply Ice: Applying ice to the area can reduce swelling and numb the pain, but avoid direct contact between the ice and skin (wrap it in cloth).
- Monitor for Shock: Broken bones and severe trauma can lead to shock, so keep the person warm, calm, and still.
Step 4: Treating Head and Neck Injuries
Head and neck injuries can be particularly dangerous, and treatment should focus on preventing further injury to the spine or brain.
- Do Not Move the Person: If there is any suspicion of a neck or spinal injury, do not move the person unless absolutely necessary. Stabilize the neck and spine to prevent further injury.
- Check for Breathing: Ensure that the person is breathing. If there are signs of a compromised airway (like difficulty breathing or gurgling), gently tilt their head back to open the airway. If the person stops breathing, begin CPR immediately.
- Monitor for Concussion Symptoms: Look for signs of a concussion, such as confusion, nausea, dizziness, or loss of consciousness. If these symptoms are present, seek immediate medical attention.
Step 5: Treating Burns
Burns from traumatic injuries, whether from fire, chemicals, or other sources, require immediate first aid to reduce the damage.
- Cool the Burn: For minor burns, cool the burn with lukewarm or cold running water for 10–15 minutes. For more severe burns, avoid applying ice, as this could damage the tissue further.
- Cover the Burn: Use a clean, non-stick bandage or cloth to cover the burn. Avoid using cotton, as it may stick to the wound.
- Prevent Infection: Don’t pop any blisters that may form. Keep the burn clean and covered until professional medical help arrives.
Step 6: Treating Chest Trauma
Chest injuries can be life-threatening, as they may involve damage to the lungs, heart, or major blood vessels.
- Assess Breathing: If the person is having difficulty breathing, help them sit in a position that makes it easier for them to breathe.
- Seal Open Wounds: If there is an open wound in the chest, seal it with a plastic or airtight material to prevent air from being drawn into the chest cavity, which could cause a collapsed lung.
- Monitor Vital Signs: Keep the person calm and monitor for signs of shock, including pale skin, rapid pulse, and shallow breathing.
Step 7: Get Professional Help
Once you’ve stabilized the injured person, it’s essential to get them to medical professionals as quickly as possible. Continue to monitor the injured person’s condition, administer first aid, and provide updates to emergency responders when they arrive.
Certification for Advanced First Aid
Learning advanced first aid techniques for treating major traumatic injuries is crucial for anyone who wants to be prepared for emergencies. The https://cprcertificationnow.com/products/first-aid-for-severe-bleeding-certification offers in-depth training on how to respond to major trauma, including techniques for handling severe bleeding, fractures, burns, and more.
By earning this certification, you’ll gain the knowledge and hands-on experience needed to respond effectively to life-threatening injuries, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring that the injured person receives the best possible care until professional help arrives.
Conclusion
In traumatic injury situations, the difference between life and death often comes down to immediate and effective first aid. By learning advanced first aid techniques, you can treat major injuries such as severe bleeding, fractures, and burns with confidence and skill. Don’t wait for an emergency to learn these critical skills—get certified today and be prepared to save a life when every second counts.